
Soil Testing
The Dirt on Healthy Crops: The Importance of Soil Testing
Crop nutrition is crucial for maximising yields, maintaining soil health, and sustaining productivity. By managing nutrient levels effectively, you also can enhance soil fertility, optimise resource use, and produce high-quality crops. Efficient nutrient management practices also promote environmental sustainability by minimising impacts on water quality and reducing resource use. As agriculture faces ongoing challenges, the importance of crop nutrition in supporting resilient and sustainable farming practices remains paramount for the future of Australian agriculture.
What is soil testing?
Soil testing for crop nutrition involves analysing soil samples to determine key indicators such as nutrient levels, organic carbon and pH balance. This process helps us to understand the specific nutrient requirements of their crops and enables them to tailor fertiliser applications accordingly. Soil testing typically involves collecting samples from various locations within a field, which are then analysed in a laboratory to assess nutrient levels such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients. The results provide valuable insights into soil fertility, allowing you to make informed decisions about nutrient management strategies, optimise fertiliser use, and maximise crop yields while minimising environmental impacts. Overall, soil testing for crop nutrition is a fundamental practice for sustainable agriculture, aiding in efficient nutrient management and ensuring the long-term productivity of farm land.
What can we find out from soil testing?
Soil testing provides crucial information about their crops’ nutrient requirements and the overall health of their soil. Here are some key insights soil testing offers:
- Nutrient Levels: Soil testing reveals the concentrations of essential nutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), sulfur (S), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and micronutrients like Zinc (Sn), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and copper (Cu). This information helps determine if their soil has adequate nutrient levels to support healthy crop growth.
- pH Level: Soil pH indicates the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, which can significantly influence nutrient availability to plants. Soil testing measures pH levels, allowing soil acidity or alkalinity to be adjusted to optimise nutrient uptake by crops.
- Nutrient Balances: By analysing nutrient levels, soil testing identifies deficiencies or excesses of specific nutrients in the soil. This information enables nutrient imbalances to be addressed through targeted fertilisation strategies, ensuring crops receive the nutrients they need for optimal growth and productivity.
- Organic matter: Organic Matter is an indicator of carbon in the soil. However, the true indication is active carbon. This is because carbon needs to be in the form of a carbo(n)hydrate (sugar). This will lead to improved microbial activity, soil structure and water holding capacity. With improved biome you will see improved mycorrhizal fungi (for phosphate uptake), improved nitrogen cycle (nitrogen availability), improved enzyme production (nutrient availability) and improved nutrient uptake. Good organic matter will also lead to improved abiotic and biotic stress resistance. Where organic matter is low you need to- ensure crop rotations, rest paddocks with a pasture ley and use organic stimulants such as fulvic, humic or seaweed extracts. Biological inoculants will see a short-term impact and should be used in conjunction with bio stimulants.
- Fertiliser Recommendations: Based on soil test results, agronomists or agricultural extension specialists can provide fertiliser recommendations tailored to the specific nutrient needs of crops and the soil’s nutrient holding capacity. This helps to inform decisions about fertiliser types, rates, and application methods, optimising nutrient use efficiency and minimising environmental impacts.
- Soil Health and Fertility: Soil testing provides insights into overall soil health and fertility, including factors such as organic matter content, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and soil texture. Assessing these parameters helps gauge the long-term productivity and sustainability of their soil and implement management practices to improve soil health over time.
- Environmental Considerations: Soil testing can also identify potential environmental risks associated with nutrient management, such as nutrient leaching or runoff, which can contribute to water pollution. By understanding nutrient dynamics in the soil, environmental impacts can be minimised while maintaining crop productivity.
Example of a Soil Testing Report:
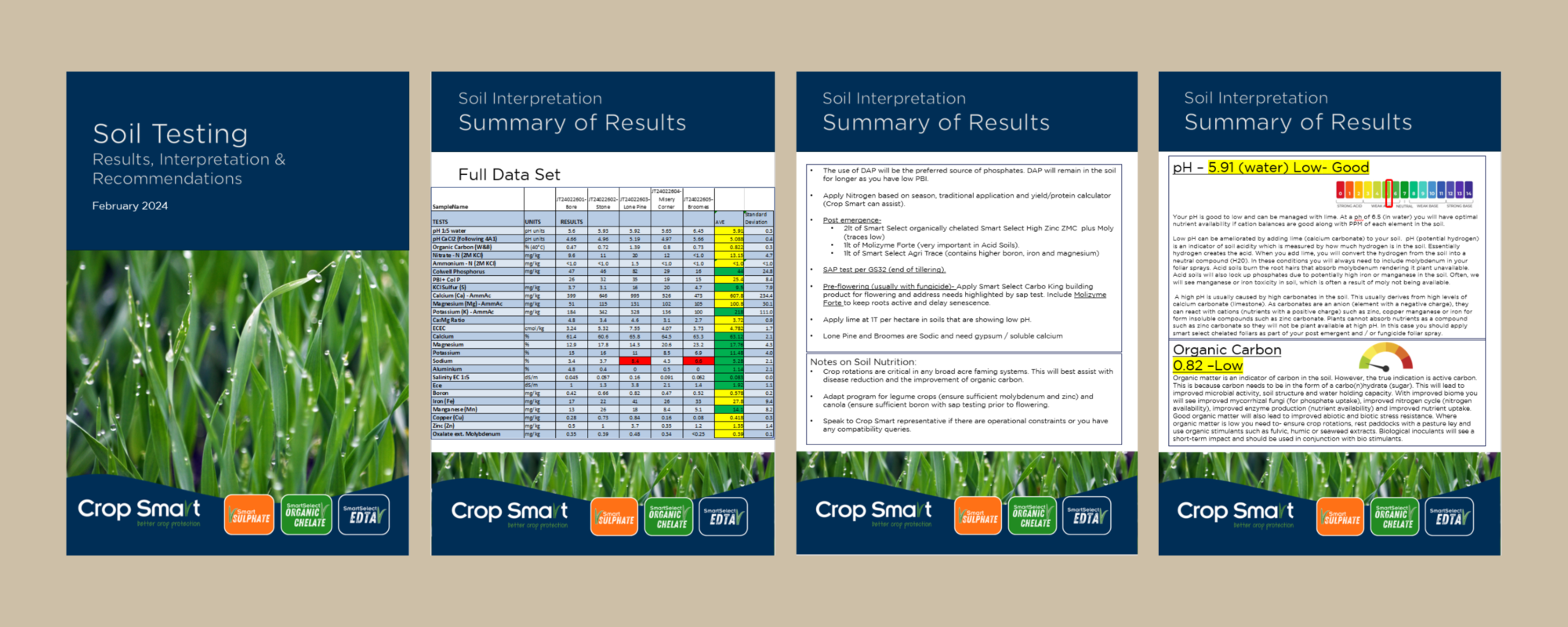
How does soil testing improve farm profitability?
Soil testing plays a crucial role in enhancing farm profitability through several key mechanisms:
- Optimised Fertiliser Use: Soil testing provides accurate information about nutrient levels in the soil, enabling fertilisers to be applied more precisely. By tailoring fertiliser applications to crop needs and soil conditions, over-application can be avoided, input costs reduced, and efficiency of nutrient use can be maximised. This targeted approach to fertiliser management helps optimise yield potential while minimising unnecessary expenses, contributing to overall profitability.
- Improved Crop Yield and Quality: By ensuring that crops have access to the right balance of nutrients, soil testing helps maximise yield potential and improve crop quality. Balanced nutrient management promotes vigorous plant growth, reduces susceptibility to diseases and pests, and enhances the nutritional content of crops. Higher yields and improved crop quality translate directly into increased marketable produce and higher returns, thereby boosting farm profitability.
- Prevention of Nutrient Imbalances: Soil testing helps identify nutrient deficiencies or excesses that can hinder crop growth and development. Addressing these imbalances through targeted fertilisation strategies ensures that crops receive the nutrients they need for optimal performance. By preventing nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, soil testing helps minimise yield losses and ensures consistent crop quality, which is essential for maintaining profitability over the long term.
- Enhanced Soil Health and Sustainability: Soil testing provides valuable insights into soil health and fertility, allowing practices to be implemented that improve soil structure, nutrient cycling, and biological activity. Healthy soils support robust root development, efficient nutrient uptake, and improved water infiltration and retention, all of which contribute to higher crop productivity and resilience to environmental stresses. By investing in soil health through informed nutrient management practices, you can sustainably increase yields, reduce input costs, and preserve the long-term productivity of their land, thus enhancing farm profitability.
- Environmental Stewardship: Soil testing helps minimise environmental impacts associated with nutrient management practices. By accurately assessing soil nutrient levels and applying fertilisers judiciously, you can reduce the risk of nutrient runoff, leaching, and groundwater contamination. Implementing environmentally responsible nutrient management practices not only helps protect natural resources but also enhances the farm’s reputation as a responsible steward of the land, which can lead to market differentiation and access to premium markets, further enhancing profitability.
Need to book a Soil Test?
Contact our Crop Nutrition specialist Ryan on 0499 112 093 or ryan@cropsmart.com.au or speak with your local Crop Smart rep for more information.








